Control Network Newsletter

Thermostat Connection Using BACnet/IP Over a Wi-Fi Connection
The BASstat wireless communicating thermostats ensure effortless integration into BACnet/IP networks, but the performance of the Wi-Fi router/access point determines how many Wi-Fi clients such as the BASstat Wi-Fi thermostat can connect to it at a time. System Integrators should measure Wi-Fi signal strength to fully leverage the BASstat capabilities.
The BAST-221C-BW2 wireless thermostat model is BACnet/IP connected using a wireless connection to a nearby Wi-Fi router/access point which supports IEEE 802.11b/g/n. The respective maximum indoor range is 115 ft. for IEEE 802.11b, 125 ft. for IEEE 802.11g, and 225 ft. for IEEE 802.11n, assuming there aren't substantial obstructions between the Wi-Fi router and the thermostats, which is the case in most standard buildings.
Some building materials rarely found in standard buildings can create obstructions which prevent Wi-Fi radios from communicating such as thick reinforced concrete (at least 200mm with or without metal reinforcement), thick masonry blocks and brick-faced walls, and metal obstructions such as shelving units or dense metal reinforcements. However, most widely used materials such as standard concrete or brick walls (100mm), lumber, plywood, and glass do not impose serious Wi-Fi radio barriers making Wi-Fi a convenient choice for many installations where wireless communication can be conveniently leveraged to avoid running wires.
Free Wi-Fi signal measuring tools such as Vistumbler can be helpful to ensure a resilient Wi-Fi connection between the thermostat and the Wi-Fi router/access point. This free tool can be installed on a laptop PC or tablet. Simply connect the laptop/tablet running Vistumbler to the Wi-Fi router/access point. Measure signal strength by moving the laptop away from it in the direction of where the Wi-Fi wireless thermostat host would be installed and monitor the signal strength graph in the tool. The tool will scan for nearby wireless networks and gives you a comprehensive report including the name, signal strength, kind of encryption, MAC address, channel the network is using, manufacturer, and more. It will also graph the traffic for each network.
Caution must be used if the same Wi-Fi router is used for IT networking and Internet access of zone occupants. One option is to create a VLAN to isolate the IT network from the OT network. However, not all Wi-Fi routers/access points support VLAN. The Wi-Fi router/access point is used to route the wireless signal from the thermostat carrying BACnet/IP messages to wired Ethernet and effectively to the building supervisor.
In the scenario below, a Wi-Fi router is used to route the wireless signal from several BAST-221C-BW2 wireless thermostats to Ethernet carrying BACnet/IP messages to the BASview3 supervisor. The BASview3 is the centralized supervisory device of the entire system communicating to the thermostats using the BACnet/IP protocol over a wired Ethernet connection.
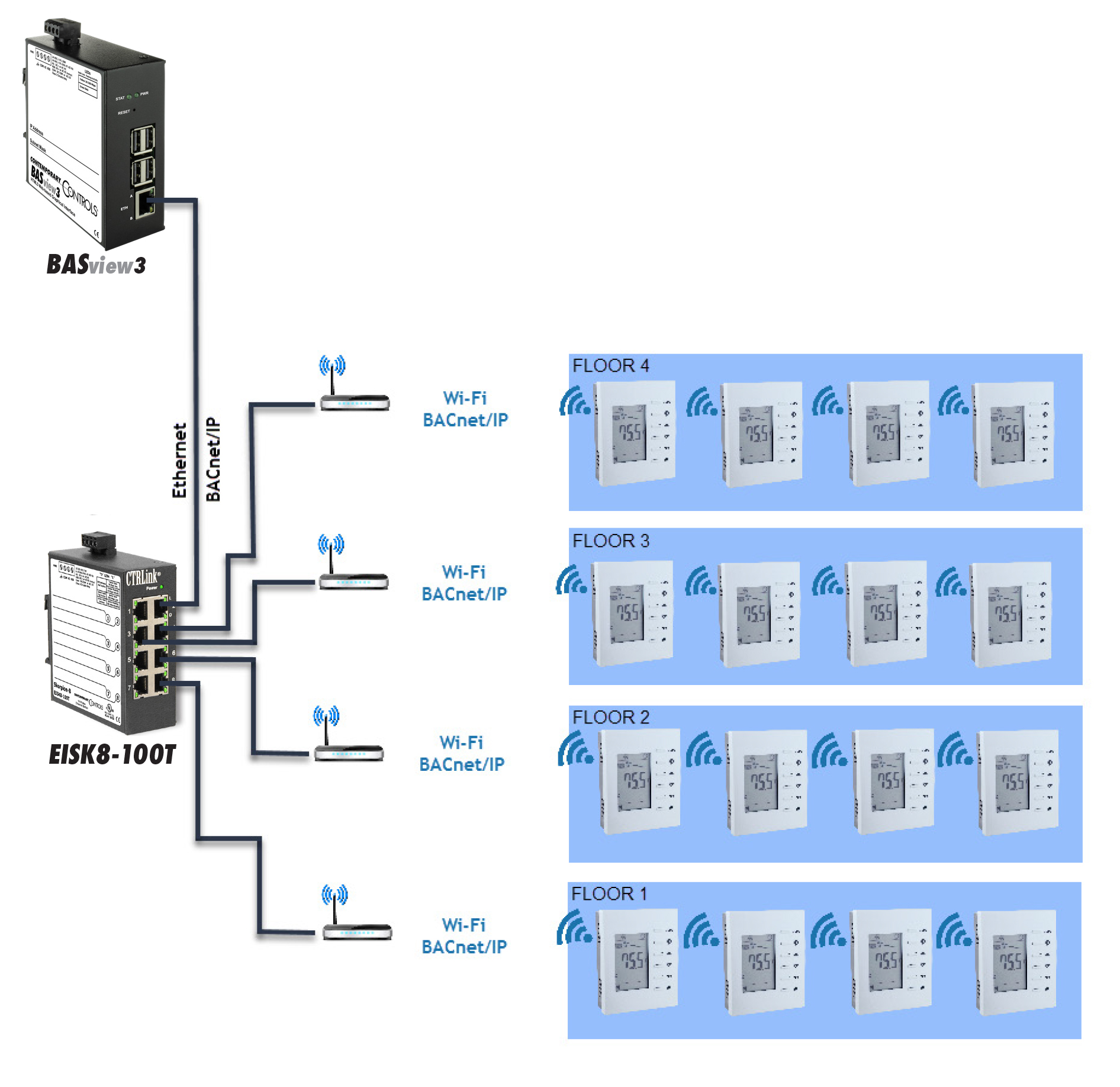
The BASview3 is a stand-alone, embedded, web-based graphical interface for building automation and process automation systems. It can be accessed from any web browser – providing supervisory functionality to any BACnet/IP system. The BASview3 is simple to install and use. Using the BASview3 with the BASstat wireless communicating thermostats provides the ideal solution for small to medium buildings or processes that require a simple-to-use graphical interface with no licensing requirements.
Visit the BASstat product page to learn more.