Control Network Newsletter

Understanding IP Router Operation
The evolution of automation control and remote connectivity has increased the demand for reliable network security. It is crucial to understand key concepts, such as IP firewall settings, port forwarding, network address translation (NAT), and gateway address settings to safeguard systems and data. In this article, we will delve into these topics and explore how they contribute to network security as well as tips for proper IP router operation.
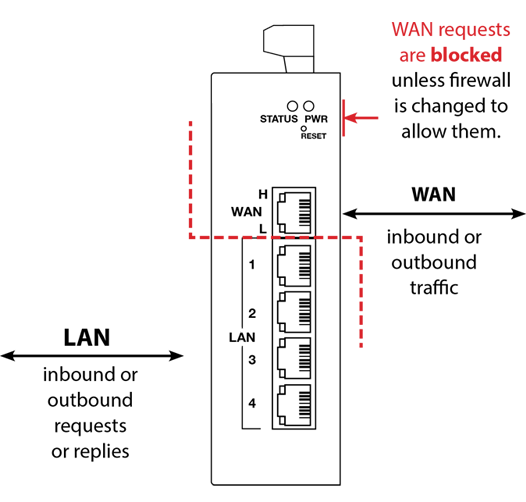 An IP firewall acts as a barrier between your network and external networks, monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. By defining rules and policies, it allows or denies access to specific IP addresses or ports. Firewall settings can be customized to suit individual security requirements and provide access to desired LAN-side devices, prevent unauthorized access, and minimize potential threats.
An IP firewall acts as a barrier between your network and external networks, monitoring and filtering incoming and outgoing traffic. By defining rules and policies, it allows or denies access to specific IP addresses or ports. Firewall settings can be customized to suit individual security requirements and provide access to desired LAN-side devices, prevent unauthorized access, and minimize potential threats.
Port forwarding is a technique that enables remote devices to traverse the firewall and access specific services or applications hosted on a private network. By configuring port forwarding settings on a router or firewall, incoming requests to a specific port are directed to a particular device within the network. This feature is commonly used for accessing webpages and applications to configure and program remote jobsite devices. It is essential to ensure that port forwarding is implemented securely, as misconfigurations can expose vulnerable services to unauthorized access.
Network address translation (NAT) is a technology that allows changing or translating IP addresses between different subnets. Usually, a WAN-side or public IP is translated to a private network to allow access to all services of a LAN-side device. This provides an added layer of security by hiding internal IP addresses from external networks, making it difficult for potential attackers to target individual devices directly. The WAN-side device can communicate to a LAN device behind the firewall without any special configuration as it uses the WAN-side IP address.
The gateway address is the IP address of the device that connects a local network to an external network, typically a router. Configuring IP address settings involves defining the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for devices within the network. This ensures proper communication between devices within the local network and establishes a secure connection with external networks. For the LAN-side devices, the gateway address should be the IP address of the LAN port of the IP router.
Understanding IP firewall settings, port forwarding, NAT, and gateway address settings is essential for maintaining a secure network environment. If the gateway address is missing or misconfigured, it will prevent internet access for the LAN-side devices. Additionally, any port forwarding and NAT settings will not work without the proper gateway address setting. Port forwarding and NAT settings provide a means to traverse the firewall – hence the firewall needs to be enabled to use these settings. If the firewall is disabled, then the router is just connecting two subnets together and the devices on either side can access each other directly using the actual IP address provided they have the correct gateway setting at both the source and destination device. Contemporary Controls' Skorpion Series of IP routers provide access to these features in an easy to configure webpage format.
To learn more, visit the Skorpion IP Routers page.